March 24, 2024

What is hair loss?
In this day and age, premature hair loss in young people is increasingly common. One of the easily recognizable signs is that the patient will lose more hair than normal. This has caused a significant amount of psychological pressure when going to work, or when appearing in public places.
Hair loss is a condition when hair falls out more than normal, especially in some areas of the scalp. After a period of time, the area of the scalp that has been shed will appear empty, smooth and lose pores. Although both men and women can experience baldness, the disease is more common in men.
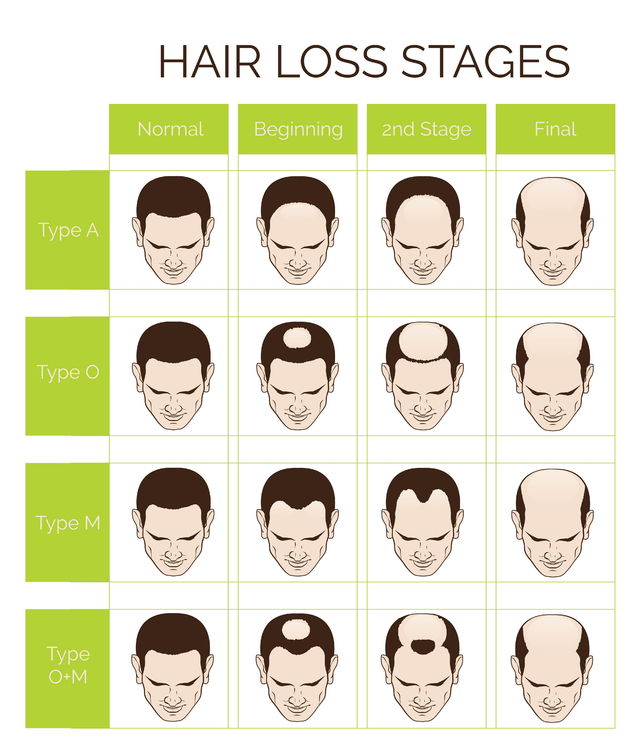
Common types of hair loss
Some common types of hair loss include:
- M-shaped pattern: hair loss concentrates on both sides of the forehead (often called bald forehead), over time it will form the letter M.
- U-shaped: hair falls out on the forehead and moves towards the top of the head, forming a U shape (another name is horseshoe shape)
- O-type: hair falls out in the middle of the top of the head, forming a circle of different sizes.
- M+O-type: hair falls out in the middle of the top of the head and on both sides of the forehead
Causes of hair loss:
1. Neuroendocrine disorders:
Hormonal imbalance is one of the most important causes of baldness. In addition, male baldness is also very much related to the male hormone testosterone.
2. Age:
When you enter middle age, your scalp will begin to secrete less oil, making your hair weak and prone to breakage, gradually leading to baldness. This is the body's natural aging process.
3. Pregnancy and breastfeeding:
For women, during pregnancy, estrogen hormone levels increase sharply, temporarily affecting the hair growth cycle. This causes women's hair to grow faster and fall out less than usual. After giving birth, estrogen levels return to normal, causing more hair to fall out, and can even cause baldness. However, hair loss after giving birth is a very natural thing. Over a while, pregnant mothers' hair will gradually grow back.
In addition, during breastfeeding, if nutrition is inadequate, the mother's body lacks some micronutrients such as calcium, iron, and zinc... which also affects hair growth.
4. Due to thyroid problems:
When your thyroid is underactive or overactive, it will lead to changes in thyroid hormones, affecting nearly every function of the body, including the hair growth cycle.
5. Stress:
Excessive stress and anxiety will also make you lose hair more easily than usual.
6. Genetics:
Hereditary baldness is common in men, often called androgenetic alopecia. If a relative is bald, then other male family members are also at high risk. Most cases of hereditary baldness are related to increased levels of male hormones, causing hair follicles to shrink, and weakening hair germ cells.
As a result, the hair growth period is shorter than normal, leading to reduced growth and increased shedding. Depending on family history, manifestations of hereditary baldness begin sooner or later.
7. Hair chemicals:
Nowadays, young people tend to dye their hair and style their hair to have an appearance that suits their preferences, as well as for personal purposes. However, using perms, relaxers or dyes, shampoos, and conditioners... can all increase the risk of hair loss and baldness.
8. Pathology:
Diseases that worsen hair loss and increase the risk of baldness such as diseases related to the thyroid gland, lupus erythematosus, diabetes, typhoid, tuberculosis... In addition, baldness in men is related to erectile dysfunction.
9. Side effects of drugs:
Some medications such as those used to treat cancer, arthritis, gout, blood pressure, depression, and cardiovascular disease can all cause hair loss.
10 Chemotherapy, radiotherapy:
The hair of cancer patients who are treated with methods such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy may not grow back as before, or grow as weak and thin hair, which is more likely to fall out.
11. Physical trauma:
When the body encounters serious problems such as an accident, surgery, weight loss, or serious illness, it also changes the hair growth and rest cycle, leading to loss or even baldness. Most people with hair conditions will grow it back after 2 - 6 months.
12. Autoimmune disease:
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that damages the hair roots leading to hair loss. In this case, the hair may or may not grow back on its own.
13. Scalp fungus:
This is ringworm of the scalp, which occurs when the fungus infects the scalp and hair shaft and causes localized scaly patches. Scalp fungus can cause scarring and prevent hair from growing back if not treated promptly.
14. Unscientific diet:
A diet lacking essential substances such as vitamins D, E, A, iron, zinc, and selenium will reduce hair health and cause excessive breakage.
15. Using many stimulants:
Abusing stimulants such as alcohol, tobacco, tea, and coffee can affect hormone levels, and change the hair growth cycle, thereby causing hair loss.
Related blog posts
Dermatology
The Growing Role of AI in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of modern life, with its influence growing rapidly, especially in healthcare.
Dermatology
Understanding Psoriasis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
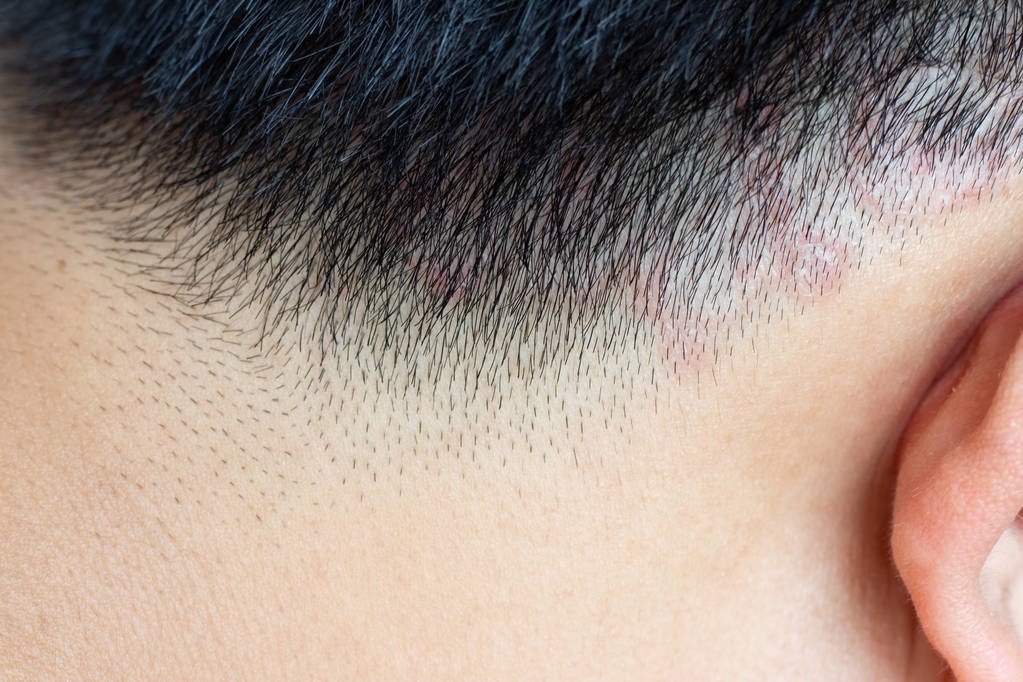
Dermatology
What is scalp ringworm?
Scalp ringworm is a fairly common skin condition. Let’s learn about scalp ringworm and how to treat it.