October 25, 2024
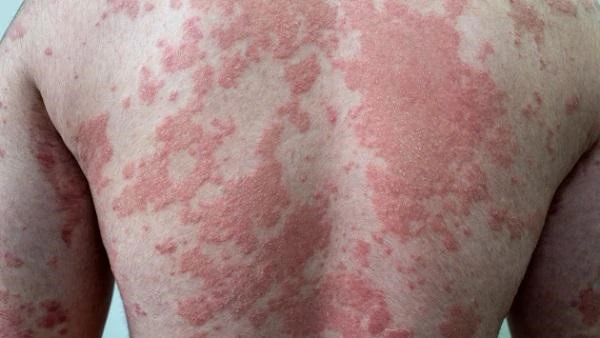
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It manifests as red, scaly patches on the skin, often accompanied by itching or discomfort. Despite its prevalence, psoriasis is often misunderstood, with many people unsure about its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. In this article, we'll explore the key aspects of psoriasis to help you better understand this condition.
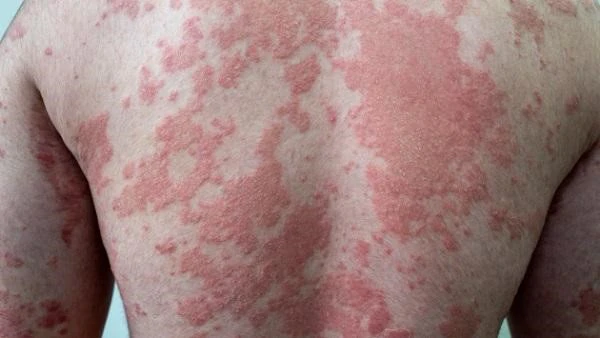
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, meaning that the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own cells. In the case of psoriasis, this results in the rapid growth of skin cells. Normally, skin cells grow and shed over a cycle of about a month, but in people with psoriasis, this process can happen in just a few days. This accelerated cell turnover leads to the buildup of skin cells on the surface, forming the characteristic plaques—thick, red patches covered with silvery-white scales.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis is still not fully understood, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Here are some of the key contributors:
1. Genetics: If you have a family member with psoriasis, your chances of developing the condition are higher. Certain genes are linked to psoriasis, though not everyone with these genes will develop the disease.
2. Immune System: Psoriasis is primarily an immune-mediated condition. T cells, which are meant to protect the body from infections, mistakenly attack healthy skin cells, triggering the rapid cell turnover that leads to psoriasis.
3. Environmental Triggers: Various environmental factors can trigger psoriasis flare-ups or worsen existing symptoms. Common triggers include stress, infections (such as strep throat), skin injuries (like cuts or sunburn), and certain medications.
4. Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices, such as smoking and heavy alcohol consumption, have been linked to an increased risk of psoriasis or more severe symptoms.
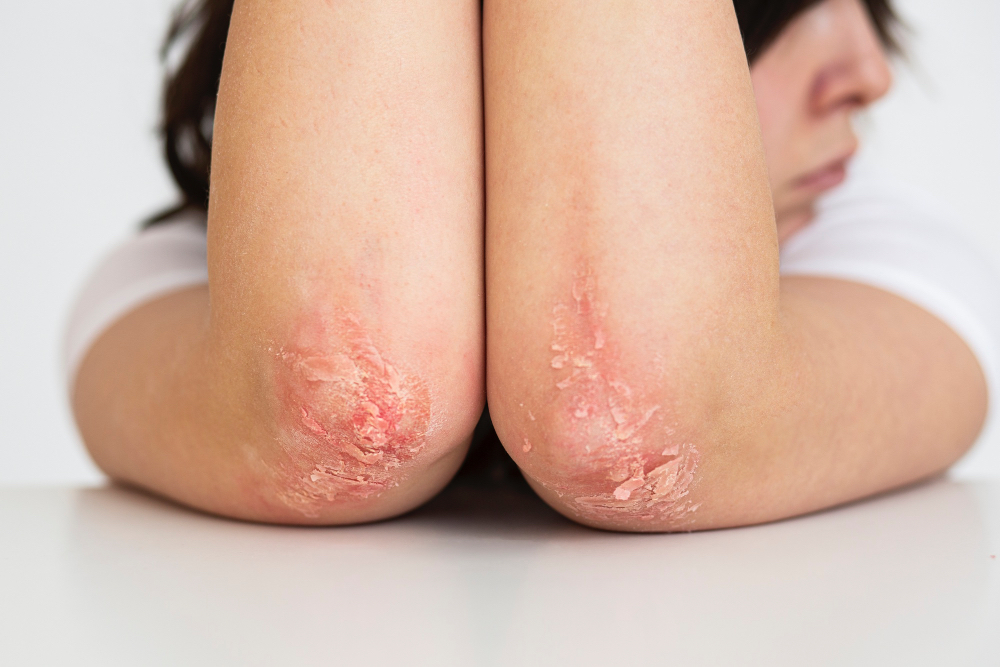
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Psoriasis symptoms can vary in severity and appearance, but some common signs include:
- Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales: These plaques can appear anywhere on the body, but are most commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
- Itching or soreness: The affected areas may be itchy or sore, leading to discomfort.
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed: The skin around the plaques can become dry and cracked, sometimes leading to bleeding.
- Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails: Psoriasis can also affect the nails, causing them to become thickened, pitted, or develop ridges.
- Joint pain or stiffness: Some people with psoriasis develop a related condition called psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain and stiffness.
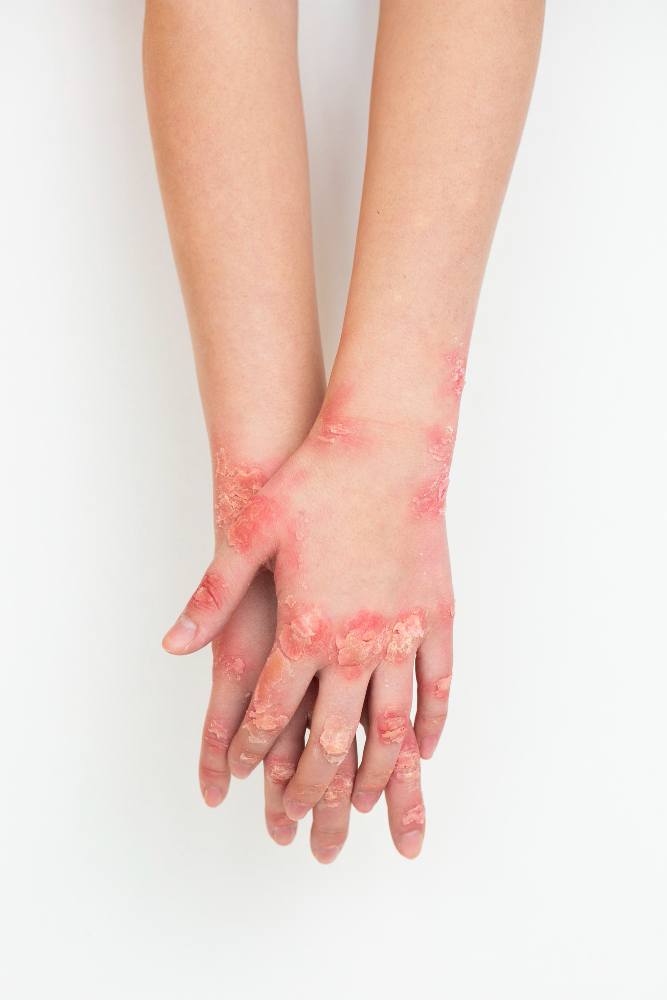

Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, each with its own set of symptoms:
1. Plaque Psoriasis: The most common form, characterized by red patches with silvery scales.
2. Guttate Psoriasis: Often triggered by a bacterial infection, this type appears as small, drop-shaped lesions.
3. Inverse Psoriasis: Found in skin folds (such as under the breasts or around the groin), this type is characterized by smooth, red patches of inflamed skin.
4. Pustular Psoriasis: This type causes white pustules (blisters of non-infectious pus) surrounded by red skin.
5. Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A rare and severe form that can cover the entire body with a red, peeling rash that can itch or burn intensely.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
While there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Treatment options include:
1. Topical Treatments: These are applied directly to the skin and are often the first line of treatment. Common topical treatments include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids. These can help reduce inflammation and slow down skin cell turnover.
2. Phototherapy: This treatment involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. Phototherapy can help reduce symptoms in moderate to severe cases of psoriasis.
3. Systemic Medications: For more severe cases, oral or injectable medications that work throughout the body may be prescribed. These include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologics, which target specific parts of the immune system.
4. Lifestyle Changes: Managing stress, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can all help manage psoriasis symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
5. Moisturizers: Regularly applying moisturizers can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce itching and scaling.
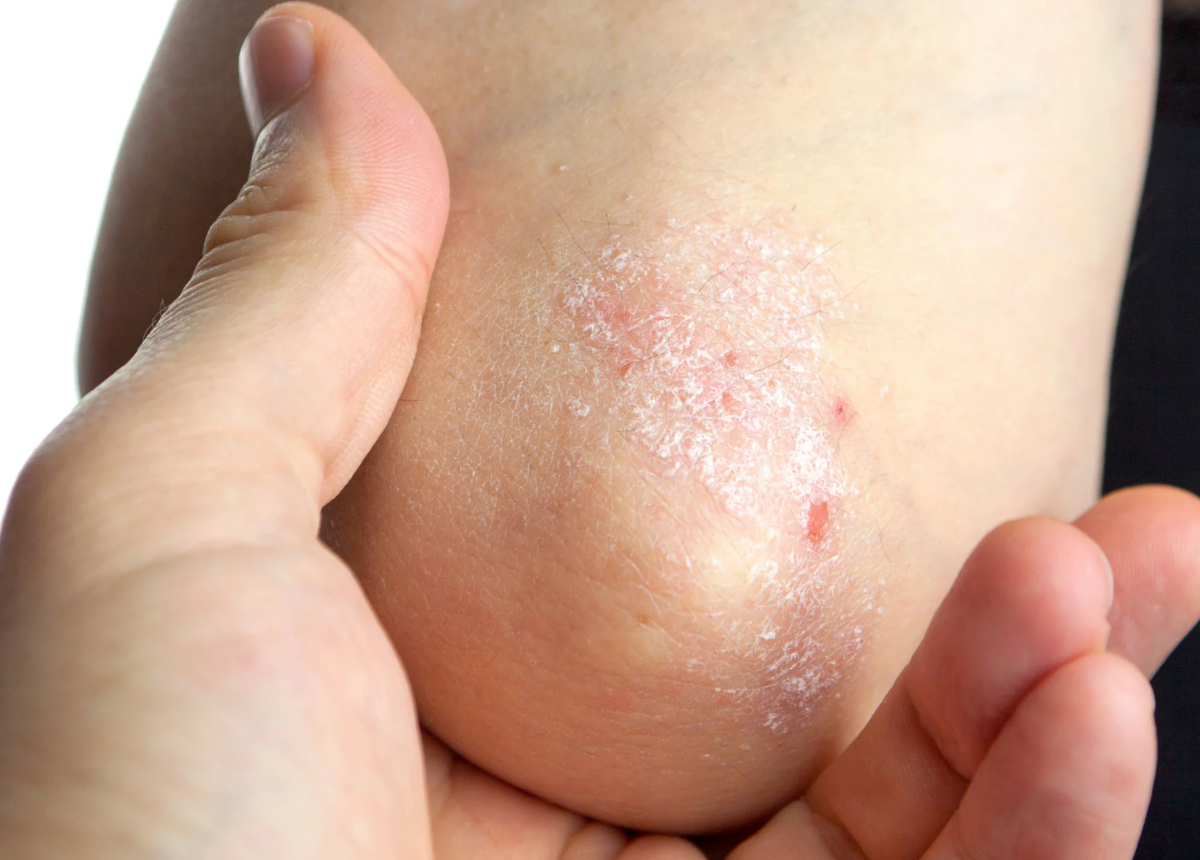
Living with Psoriasis
Psoriasis can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, both physically and emotionally. It's important for those with psoriasis to seek support, whether from healthcare professionals, support groups, or loved ones. Learning to manage the condition through a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments can help reduce symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a complex, chronic condition that requires ongoing management. By understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring various treatment options, individuals with psoriasis can take proactive steps to manage their condition and lead a healthier life. If you suspect you have psoriasis or if your symptoms worsen, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Related blog posts
Dermatology
The Growing Role of AI in Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become an integral part of modern life, with its influence growing rapidly, especially in healthcare.
Dermatology
What is scalp ringworm?
Scalp ringworm is a fairly common skin condition. Let’s learn about scalp ringworm and how to treat it.

Dermatology
Your Ultimate Guide to Managing Hair Loss
Hair loss is a common experience that can impact your confidence, but understanding its causes and adopting the right hair care products can make a significant difference.